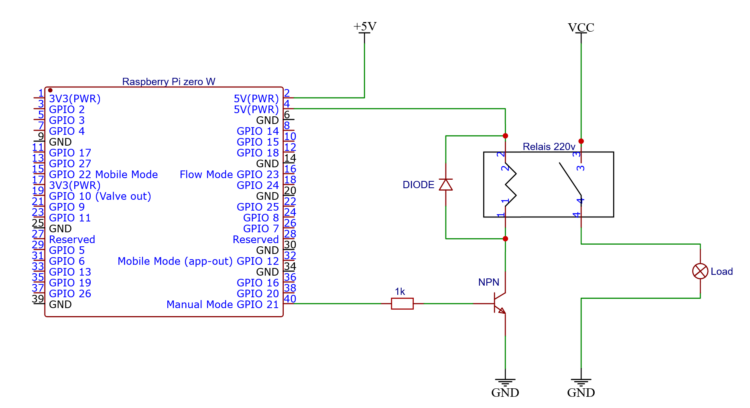
The first is by using an NPN-transistor, and the second a N-channel-MOSFET. Both circuits are pretty much the same otherwise.
NPN transistor
Using a transistor is the cheapest and fail proof way of doing this. Setting a output pin high on your CPU sends a resistor limited current to the base of the transistor.
A multiple of that current is allowed through through the transistor and therefore the relay-coil, powered from the same voltage source as the CPU, but not through it.
N-Channel MOSFET
We can use a N-channel MOSFET as a bottom-side-switch. But not all MOSFETs are created equal. A lot of them do not even switch on partially with only 3.3v on their gate.
According to the datasheet, the FB4410Z from IRF (which I have) can supply more than 1 amp with only 3.3v on its gate.

Can’t do this without a diode
A voltage spike would kill our MOSFET or transistor. When we turn the relay of the coil remains charged, because it also is an inductor, it will produce a spike on the bottom side.
The diode provides a path back into the coil. The voltage drop over the diode will bleed of the excess energy.
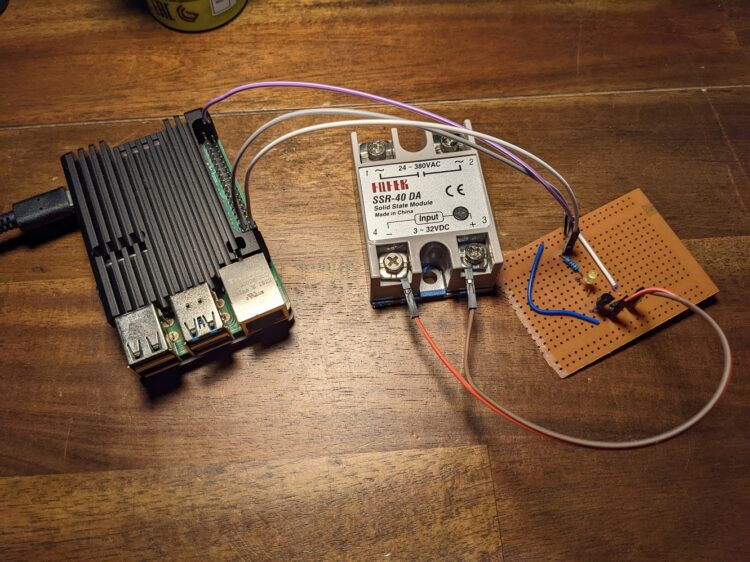
Prototype
Conclusion
With the help of a transistor or MOSFET, we are now free to drive any relay we want directly from a digital IO pin. We can even switch some really big relays capable of 80 amps or more.
